*File Formats
A file format is a standard way that information is encoded for storage in a computer file. It specifies how bits are used to encode information in a digital storage medium. File formats may be either proprietary or free and may be either unpublished or open.
There are File formats for:
- Images
- Sounds
- Movies
- Documents
- Miscellaneous
*Resolution
In information technology, "lossy" compression is the class of data encoding methods that uses inexact approximations (or partial data discarding) for representing the content that has been encoded. Such compression techniques are used to reduce the amount of data that would otherwise be needed to store, handle, and/or transmit the represented content. The different versions of the photo of the cat at the right demonstrate how the approximation of an image becomes progressively coarser as more details of the data that made up the original image are removed. The amount of data reduction possible using lossy compression can often be much more substantial than what is possible with lossless data compressiontechniques.
Using well-designed lossy compression technology, a substantial amount of data reduction is often possible before the result is sufficiently degraded to be noticed by the user. Even when the degree of degradation becomes noticeable, further data reduction may often be desirable for some applications (e.g., to make real-time communication possible through a limited bit-rate channel, to reduce the time needed to transmit the content, or to reduce the necessary storage capacity).
Lossy compression is most commonly used to compress multimedia data (audio, video, and still images), especially in applications such as streaming media and internet telephony. By contrast, lossless compression is typically required for text and data files, such as bank records and text articles. In many cases it is advantageous to make a master lossless file that can then be used to produce compressed files for different purposes; for example, a multi-megabyte file can be used at full size to produce a full-page advertisement in a glossy magazine, and a 10 kilobyte lossy copy can be made for a small image on a web page.
Images
-Raster = Bitmap
-Vector = Line
Pixel = Picture Element
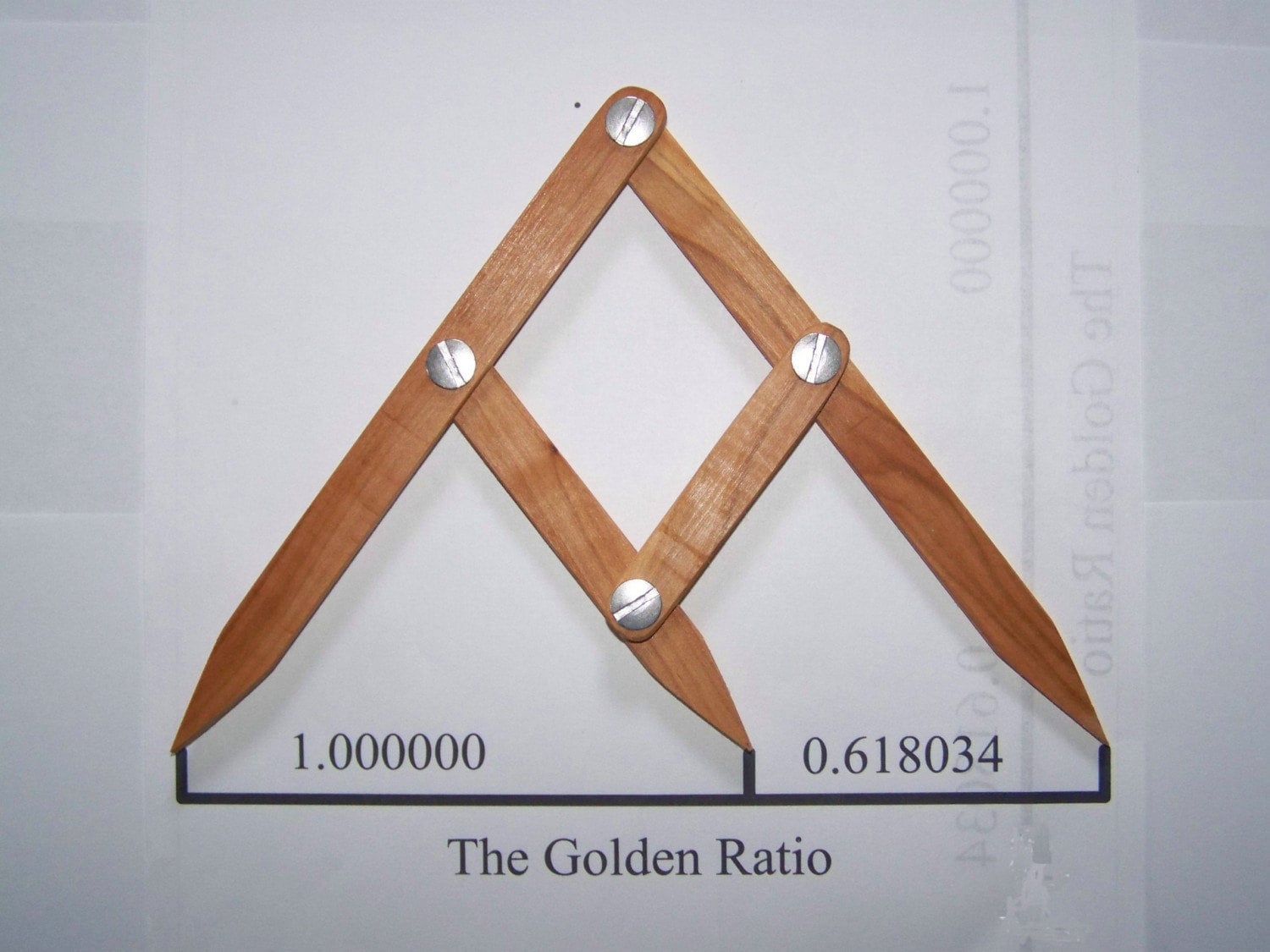
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. The figure on the right illustrates the geometric relationship. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
where the Greek letter phi (φ) represents the golden ratio. Its value is:
The golden ratio is also called the golden section (Latin: sectio aurea) or golden mean. Other names include extreme and mean ratio, medial section, divine proportion, divine section (Latin: sectio divina), golden proportion, golden cut, and golden number.
Divine Proportion - Arm
Human Body
Face
Architecture
Art

No comments:
Post a Comment